Competency 2: Identification and Remediation of Disabilities
Identification and Remediation
Here you will find the 4 key aspects of Identifying and remediating disabilities. These include:
- Response to Intervention (RTI)
- Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
- Universal Design Learning (UDL)
- Assistive Technology (AT)
RTI
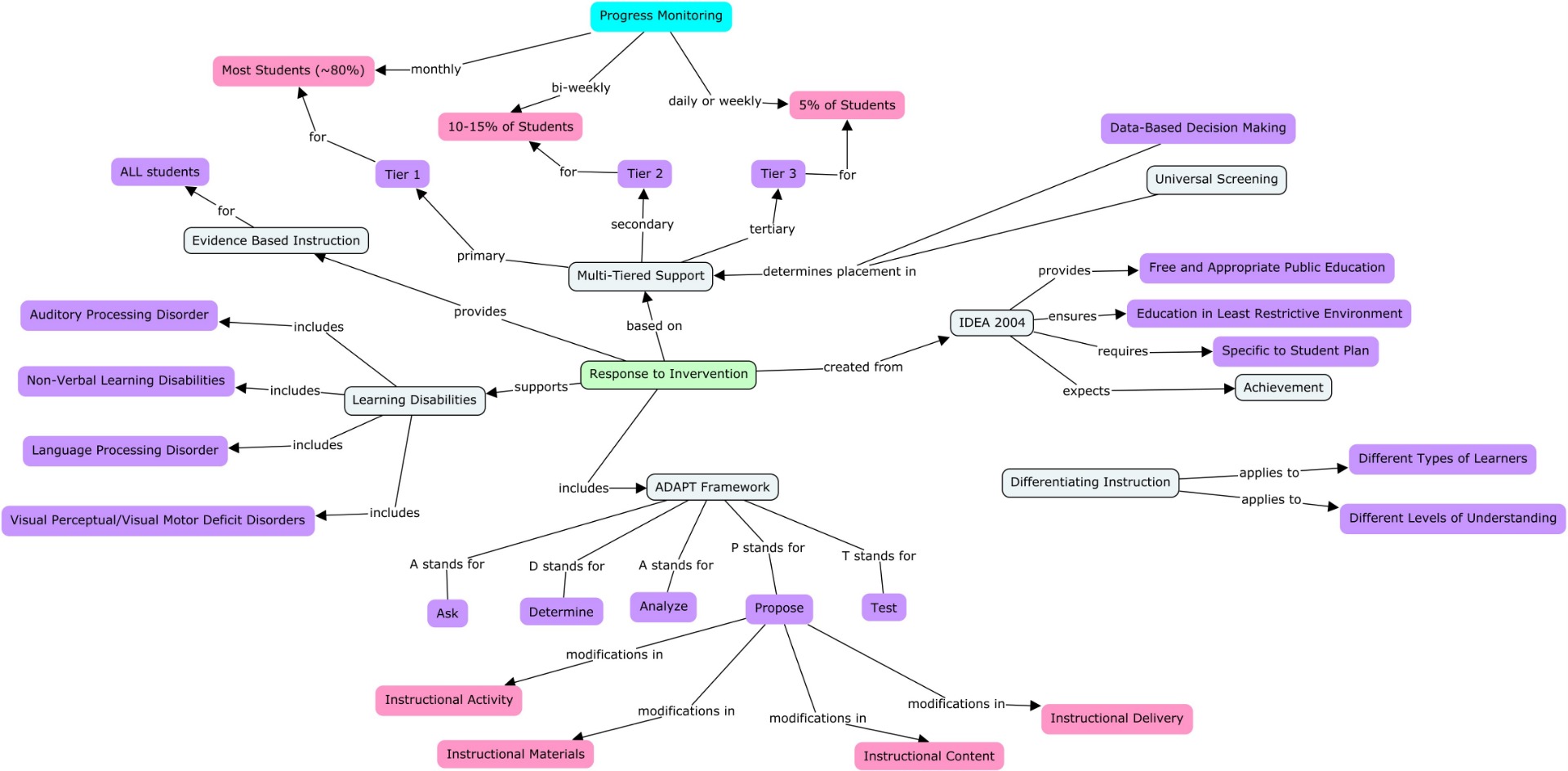
Below is the RTI Pyramid, displaying the different levels of intervention.
Figure 1. Response to Intervention Pyramid. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://eghs.d214.org/staff/rti-response-to-intervention/
Earlier in the year I chose to complete an IRIS module on response to intervention and mathematics. In this module, I learned many skills on how to implement response to intervention programs into my general education mathematics classroom in order to further my students understanding. Initially, I thought it would be a great idea to allow the student in tier 2 and 3 (i.e. those displaying that they are struggling) time in resource room or something of a similar caliber, with an experienced math teacher. Furthermore, while going through this module I found the myth about students lack in motivation to be very solid. To me it is obvious that a student starts to lack motivation when they are struggling and feel hopeless. This is why RTI is so important even in secondary classrooms. I liked the dual discrepancy and would use this progress monitoring tactic in my classroom. This allows for students to be measure on both growth and/or proficiency to prove their learning.
I found it very important to note how to make the decision on whether a student is struggling and needs extra assistance. By the dual discrepancy model, a student must either display proficiency (the number of correct response) and/or growth (the slope of the number of correct responses per week). By graphing the student's performance and comparing it to standards set in place we are able to clearly see if what we have been doing helps the child. For example, if a student is receiving tier 2 supports and does not meet the proficiency criteria but does have adequate progress made (growth) then we determine that the student is receiving the appropriate degree of help and should stay where they currently are.
IEP
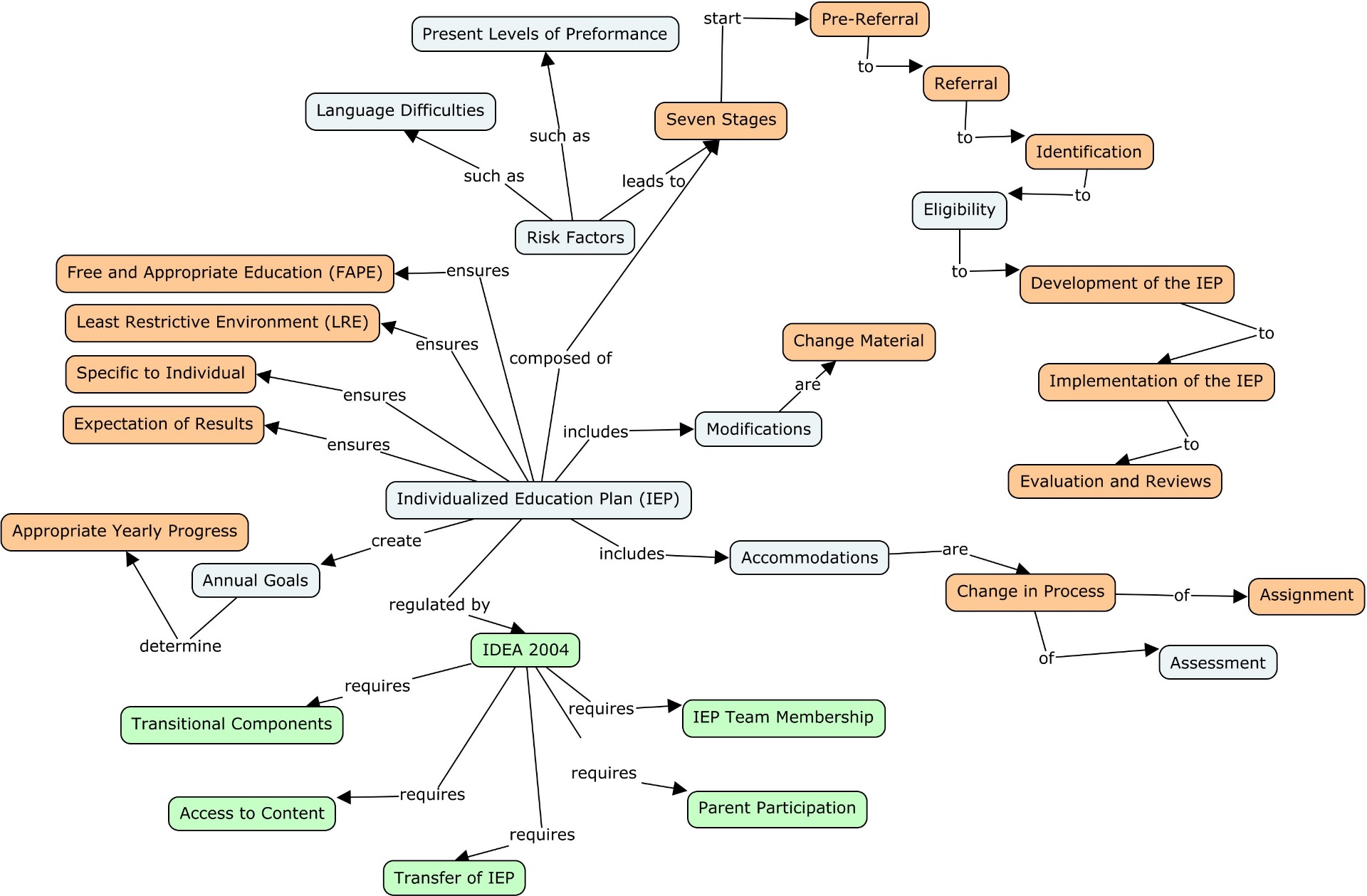
For more information on the opinions of students with IEPs and parents see competency 4.
UDL
UDL stands for Universal design learning. this is an educational approach to design and implementation. New research the brain along with new media technologies has result in a way to respond to learner diversity. The is Universal Design Learning. In UDL. it is assumed that student diversity is the norm.
This contradicts the inflexible "one-size-fits-all" curricula, where barriers to learning arise often. The goal of UDL is to create a system that minimizes or even gets rid of those barriers.
In my work through the year I came across a video in one of Dr. Raimondi's Slides I would like to share. See the video below.
For more on Universal Design Learning visit The National Center on Universal Design for Learning at https://www.udlcenter.org/
AT
Below are some fantastic resources on assistive technology and how it is used for special education students in the classroom.
Assistive Technology Advocacy- https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B1mdRDzIaULfVE1hSTRyUlVMR0E/edit?usp=sharing
Assistive Technology and Universal Design for Learning: Two Sides of the Same Coin -https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B1mdRDzIaULfRnBqWk1nS0NIZlk/edit?usp=sharing
AT Consideration Guide for IEP Teams -https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B1mdRDzIaULfVEJaSXB4ZUhnUTQ/edit?usp=sharing
Conducting an AT assessment -https://techpotential.net/assessment
AT tools - https://www.ldonline.org/article/6240